This post follows Teleport’s official Kubernetes Access “Getting Started” flow, using the Web UI guided enrollment (Helm) and validating access with a non-admin Teleport user.
This Post Is Based On
Lab Context
Teleport (Community Edition)
- Proxy / Web UI:
https://teleport.maksonlee.com - Proxy port:
443 - Teleport version (example):
18.6.4 - Setup user (UI login):
teleport-admin(local user)
Kubernetes (bare-metal kubeadm HA)
- Admin node for Helm + kubectl:
k8s-1 - Teleport agent namespace:
teleport-agent - Kubernetes cluster name in Teleport:
homelab-k8s
What You’ll Do
- Create a Teleport role
kube-access - Assign
kube-accessto:teleport-admin(for UI enrollment)teleport-test(for final testing)
- Create Kubernetes RBAC for group
viewers - Use Teleport UI to generate and run the Helm install command
- Set up access in UI (groups =
viewers) - Test with
teleport-testusingtsh+kubectl
- Create the Teleport role
kube-access
Create kube-access.yaml on the Teleport server:
kind: role
metadata:
name: kube-access
version: v7
spec:
allow:
kubernetes_labels:
'*': '*'
kubernetes_resources:
- kind: '*'
namespace: '*'
name: '*'
verbs: ['*']
kubernetes_groups:
- viewers
deny: {}
Apply it:
sudo tctl create -f kube-access.yaml
Do NOT use kubectl on this file. It’s a Teleport role, not Kubernetes YAML.
- Assign
kube-accesstoteleport-adminandteleport-test
We assign the role to two users:
teleport-admin: the user you log into the Web UI with to enroll/configure Kubernetes accessteleport-test: a non-admin user used to validate Kubernetes access end-to-end
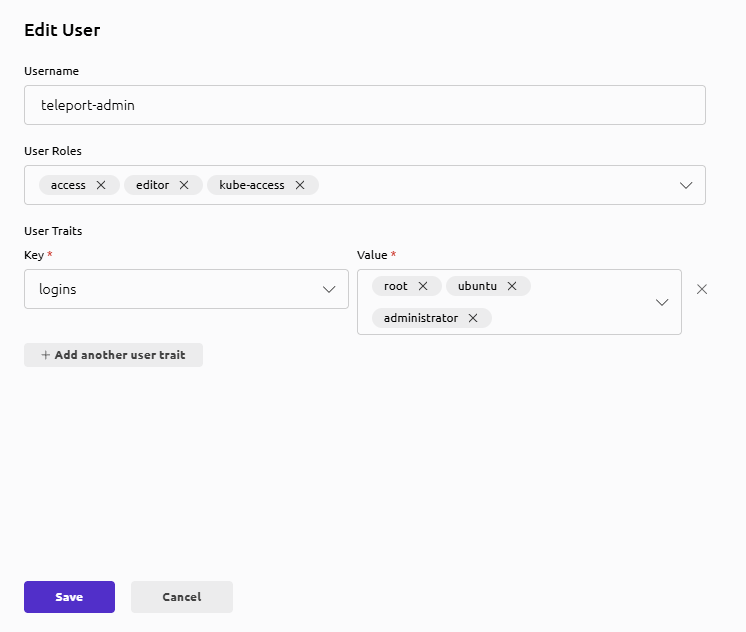
Add kube-access to teleport-admin (UI recommended)
- Identity → Users → teleport-admin → Edit
- Add role:
kube-access - Save
If teleport-admin already has access and editor, it should become: access, editor, kube-access.
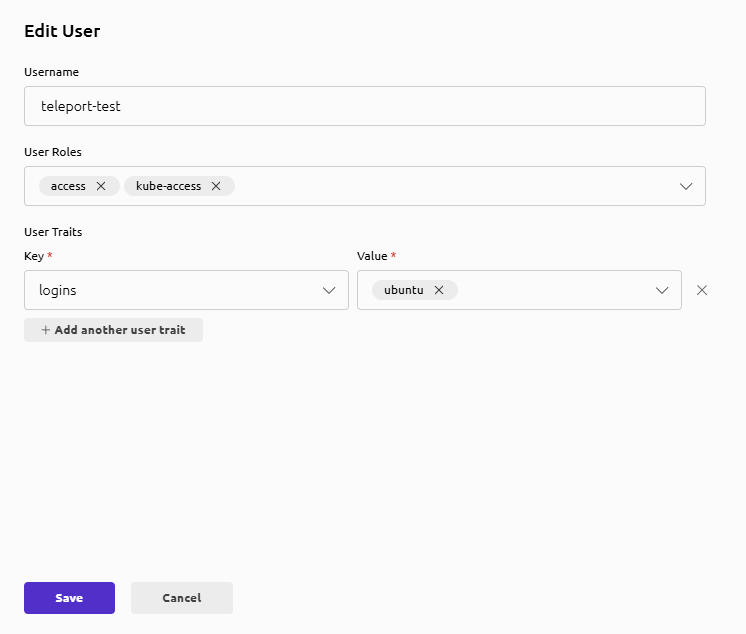
Create teleport-test and assign kube-access
If teleport-test does not exist yet:
sudo tctl users add teleport-test \
--roles=access,kube-access \
--logins=ubuntu
Open the printed invite URL, set password + MFA, then complete onboarding.
If teleport-test already exists, ensure its roles include:
accesskube-access
(UI path: Identity → Users → teleport-test → Edit)
- Create Kubernetes RBAC for group
viewers
On k8s-1, create viewers-bind.yaml:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: viewers-crb
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: viewers
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: view
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Apply it:
kubectl apply -f viewers-bind.yaml
This grants read-only access to Kubernetes group viewers.
- Enroll the Kubernetes cluster using Teleport Web UI (Helm)
- Log in to Teleport Web UI as
teleport-admin - Go to Add New → Kubernetes
- In Configure Resource, run:
helm repo add teleport https://charts.releases.teleport.dev && helm repo update
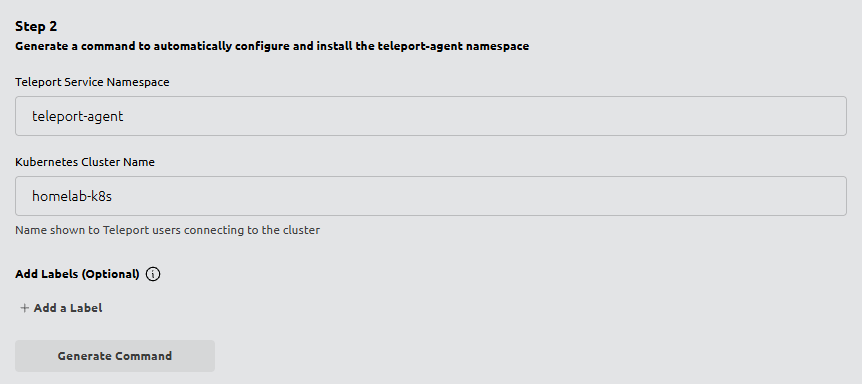
- Set:
- Teleport Service Namespace:
teleport-agent - Kubernetes Cluster Name:
homelab-k8s
- Teleport Service Namespace:
- Click Generate Command
- Run the generated script on
k8s-1
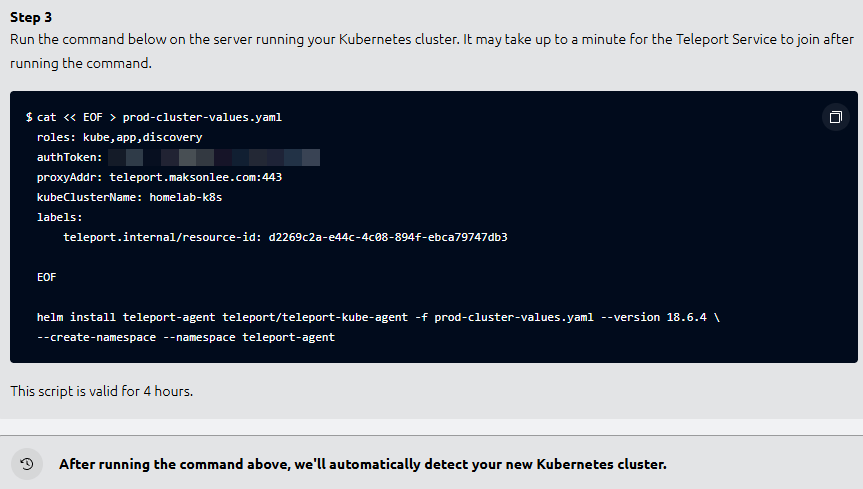
Your UI-generated command pattern looks like:
cat << EOF > prod-cluster-values.yaml
roles: kube,app,discovery
authToken: <REDACTED_JOIN_TOKEN>
proxyAddr: teleport.maksonlee.com:443
kubeClusterName: homelab-k8s
labels:
teleport.internal/resource-id: <REDACTED_RESOURCE_ID>
EOF
helm install teleport-agent teleport/teleport-kube-agent -f prod-cluster-values.yaml --version 18.6.4 \
--create-namespace --namespace teleport-agent
Verify:
kubectl get pods -n teleport-agent -o wide
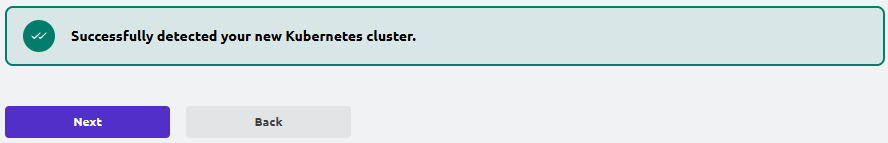
Back in the UI, you should see:
- “Successfully detected your new Kubernetes cluster.”
Note: Enrolling a Kubernetes node as an SSH host after kube-agent is installed
If you later enroll a Kubernetes worker node (for SSH access) using the UI “Enroll SSH Server” script, you may hit:
Warning: Teleport appears to already be running on this host (pid: …)
This is expected on Kubernetes nodes because the teleport-kube-agent Pod also runs a teleport process on that node. The guided SSH enrollment script can’t reliably tell whether Teleport is running in a Pod vs already installed on the host, so it exits to avoid clobbering an existing install.
Fix: run the SSH enroll script with “ignore checks”
Add -i:
sudo bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://teleport.maksonlee.com/scripts/<SSH_ENROLL_TOKEN>/install-node.sh)" -- -i
Use -i only when the “already running” warning is caused by the Kubernetes teleport-agent Pod.
- Set Up Access in the UI
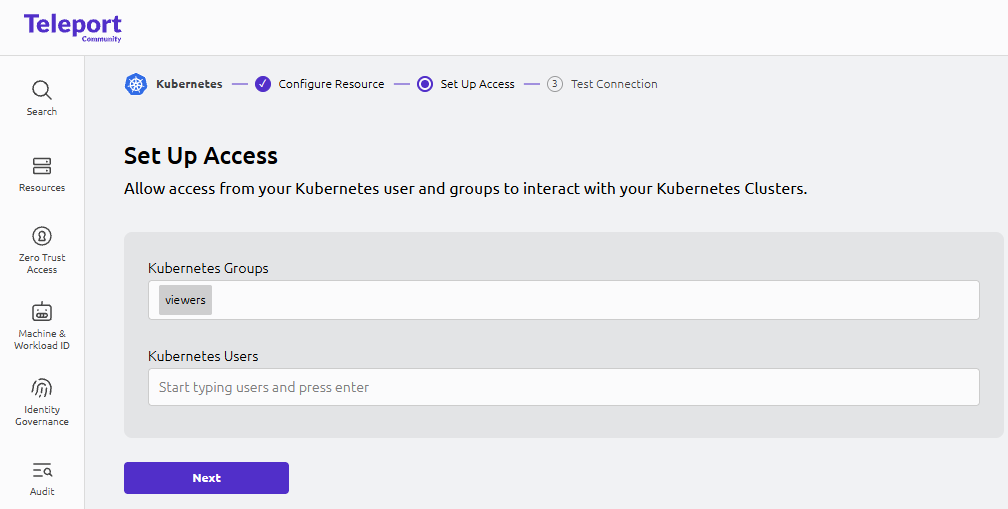
In the Set Up Access page:
- Kubernetes Groups:
viewers - Kubernetes Users: (leave empty)
Click Next.
- (Optional) UI “Test Connection”
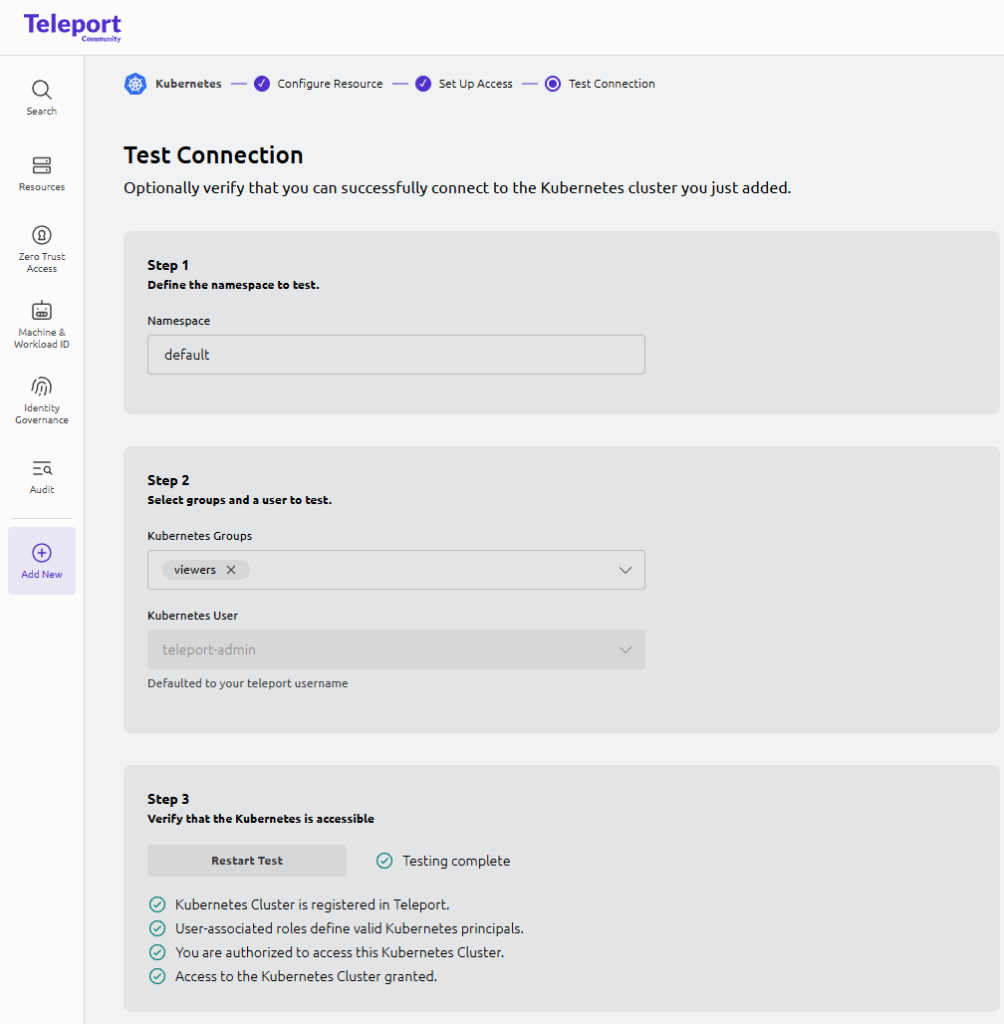
The UI test often defaults the Kubernetes user to the currently logged-in Teleport username (teleport-admin). That’s fine as a connectivity sanity check.
- Final test with
teleport-test(recommended)
On your workstation (or any host with tsh + kubectl):
tsh logout || true
tsh login --proxy=teleport.maksonlee.com:443 --auth=local --user=teleport-test teleport.maksonlee.com
tsh kube ls
tsh kube login homelab-k8s
kubectl get ns
kubectl get pods -A
Confirm read-only enforcement:
kubectl create ns should-fail
Did this guide save you time?
Support this site