This post shows how I deploy Argo CD v3.2.2 into my bare-metal kubeadm Kubernetes cluster, expose it through Traefik at:
https://argocd.maksonlee.com
…and manage it from k8s-1 using the Argo CD CLI (because that’s where kubectl lives in my lab).
What you’ll build
- Namespace:
argocd - Argo CD installed from the official manifest (pinned to v3.2.2)
- Argo CD exposed via Traefik IngressRoute (UI + CLI gRPC on the same hostname)
- TLS terminated by Traefik using my existing wildcard certificate
*.maksonlee.com - First app deployed via Argo CD CLI (
guestbook)
Prerequisites
This post assumes you already have:
- A working bare-metal Kubernetes cluster (kubeadm + containerd)
- MetalLB providing Traefik’s LoadBalancer IP on your LAN (example:
192.168.0.98) - Traefik installed as the default Ingress controller
- HTTPS already enabled in Traefik using a wildcard Let’s Encrypt cert (
*.maksonlee.com) configured as Traefik’s default TLS certificate
Related foundation posts (for context):
DNS
Create a DNS record (or LAN DNS override) so Argo CD routes through Traefik:
192.168.0.98 argocd.maksonlee.comBecause Traefik is already serving *.maksonlee.com via a wildcard cert, argocd.maksonlee.com will automatically be covered.
- Install Argo CD (v3.2.2)
Run everything on k8s-1 (my admin node that already has kubectl configured).
Create namespace + apply the official manifest:
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd \
-f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/v3.2.2/manifests/install.yamlWait for pods:
kubectl get pods -n argocd -wYou should see core components become Running:
argocd-serverargocd-repo-serverargocd-application-controllerargocd-applicationset-controllerargocd-redisargocd-dex-serverargocd-notifications-controller
- Install the Argo CD CLI on k8s-1
Since kubectl lives on k8s-1, install the Argo CD CLI there as well.
Pin to v3.2.2:
VERSION=v3.2.2
curl -sSL -o argocd-linux-amd64 \
https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd/releases/download/$VERSION/argocd-linux-amd64
sudo install -m 555 argocd-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/argocd
rm -f argocd-linux-amd64
argocd version --client- Run Argo CD behind Traefik (TLS terminated at Traefik)
Because Traefik already terminates HTTPS for *.maksonlee.com, I run argocd-server in insecure mode behind Traefik (HTTP inside the cluster, HTTPS at the edge).
Patch argocd-cmd-params-cm:
kubectl -n argocd patch configmap argocd-cmd-params-cm --type merge -p '{
"data": {
"server.insecure": "true"
}
}'Restart argocd-server:
kubectl -n argocd rollout restart deploy/argocd-server
kubectl -n argocd rollout status deploy/argocd-serverOptional (recommended): set Argo CD’s external URL (useful for links and future SSO/OIDC redirects):
kubectl -n argocd patch configmap argocd-cm --type merge -p '{
"data": {
"url": "https://argocd.maksonlee.com"
}
}'- Expose Argo CD via Traefik IngressRoute (UI + CLI gRPC)
Argo CD uses:
- normal web traffic for the UI/API
- gRPC for many CLI operations
With Traefik, the simplest working pattern is:
- Route all traffic for
argocd.maksonlee.comtoargocd-server:80 - Route gRPC traffic (identified by
Content-Type: application/grpc) to the same service using h2c
Create argocd-ingressroute.yaml:
apiVersion: traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: IngressRoute
metadata:
name: argocd-server
namespace: argocd
spec:
entryPoints:
- websecure
routes:
- kind: Rule
match: Host(`argocd.maksonlee.com`)
priority: 10
services:
- name: argocd-server
port: 80
- kind: Rule
match: Host(`argocd.maksonlee.com`) && Header(`Content-Type`, `application/grpc`)
priority: 11
services:
- name: argocd-server
port: 80
scheme: h2c
# TLS is handled by Traefik.
# With a default TLSStore wildcard cert already configured in Traefik, no secretName is needed here.
tls: {}Apply it:
kubectl apply -f argocd-ingressroute.yamlNow Argo CD should be reachable at:
https://argocd.maksonlee.com
- First login (default user + initial password)
Default user
The default username is:
- admin
Get the initial password
argocd admin initial-password -n argocdLogin using the CLI
argocd login argocd.maksonlee.comAt the prompts:
- Username:
admin - Password: (paste the initial password output)
If your environment ever has gRPC issues through proxies, try:
argocd login argocd.maksonlee.com --grpc-web- Change the admin password and remove the bootstrap secret
Immediately change the password:
argocd account update-passwordThen delete the initial admin secret (it’s only needed for first login):
kubectl -n argocd delete secret argocd-initial-admin-secret- Create and sync a test app (guestbook)
In the getting started guide, Argo CD’s canonical demo app is guestbook.
Set your kubectl default namespace (optional convenience):
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=argocdCreate the app:
argocd app create guestbook \
--repo https://github.com/argoproj/argocd-example-apps.git \
--path guestbook \
--dest-server https://kubernetes.default.svc \
--dest-namespace defaultCheck status:
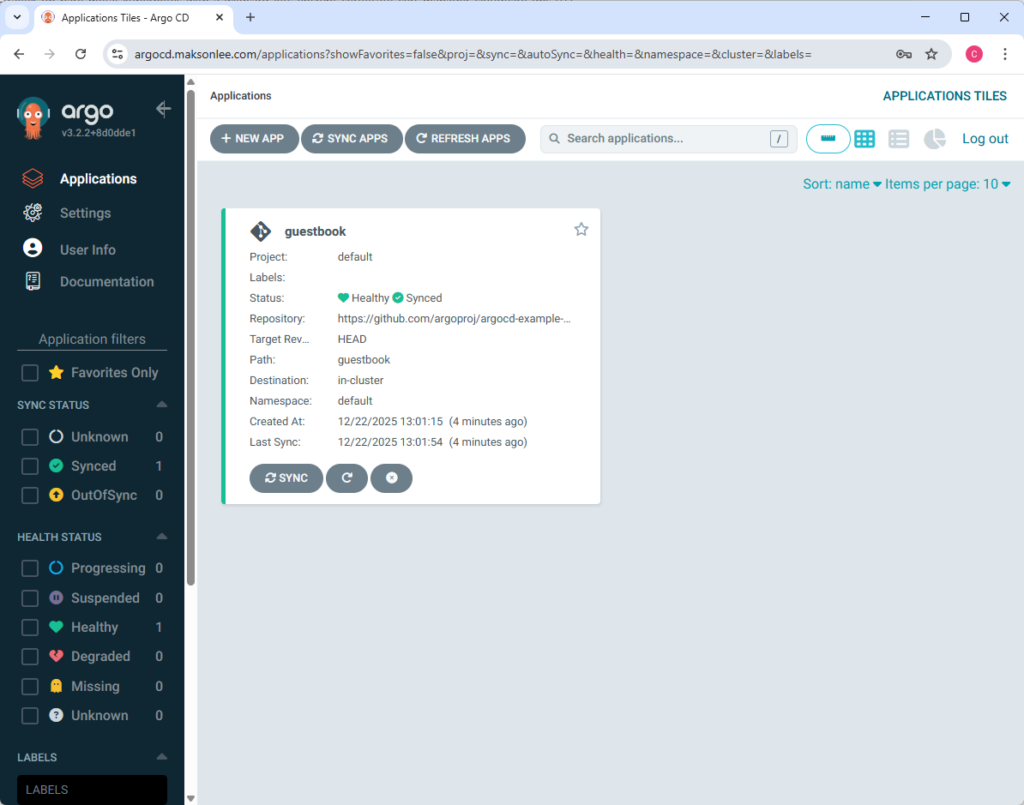
argocd app get guestbookYou’ll usually see it as OutOfSync / Missing before the first sync.
Sync it (deploy the resources):
argocd app sync guestbookAfter sync, the app should become Synced and eventually Healthy.
Summary
You now have:
- Argo CD installed in
argocdnamespace (v3.2.2) - Argo CD exposed via Traefik at
https://argocd.maksonlee.com - Wildcard TLS handled at Traefik (no per-app TLS config required)
- Argo CD CLI installed on k8s-1 and working end-to-end
- A test app (
guestbook) deployed via GitOps using Argo CD
Did this guide save you time?
Support this site