This guide builds a 3-node Kubernetes cluster on bare-metal Ubuntu Server 24.04, where:
- All three machines run both control-plane and worker components (stacked etcd).
- kube-vip exposes a floating API VIP (
k8s.maksonlee.com → 192.168.0.97) for kubectl clients. - MetalLB (Layer 2 mode) provides a LoadBalancer IP on your LAN (
192.168.0.98). - Traefik runs as the Ingress controller, exposed via MetalLB, with 3 replicas (one per node) for basic HA.
- Apps are reached via:
app1.maksonlee.com → 192.168.0.98app2.maksonlee.com → 192.168.0.98
Everything is done with kubeadm and containerd. No cloud, no managed load balancer, just three bare-metal Ubuntu boxes on your LAN.
Lab Overview (Bare Metal)
Three bare-metal Ubuntu 24.04 servers, each acting as both control-plane and worker:
- OS: Ubuntu Server 24.04 on all three nodes
- Hostnames / IPs (examples):
k8s-1.maksonlee.com–192.168.0.99k8s-2.maksonlee.com–192.168.0.100k8s-3.maksonlee.com–192.168.0.101
- Container runtime:
containerd.io(from Docker apt repo),SystemdCgroup = true - Kubernetes:
kubeadm,kubelet,kubectlfrompkgs.k8s.io(v1.34) - Pod CIDR:
10.244.0.0/16(Calico) - Service CIDR:
10.96.0.0/12(kubeadm default) - Kubernetes control-plane endpoint:
k8s.maksonlee.com:6443(VIP 192.168.0.97 announced by kube-vip) - kube-vip API VIP:
192.168.0.97 - MetalLB IP pool:
192.168.0.98-192.168.0.98(used for Traefik) - Ingress hosts:
app1.maksonlee.com → 192.168.0.98app2.maksonlee.com → 192.168.0.98
- Network interface on all nodes:
ens32 - LAN clients live in the same
192.168.0.0/24network.
Prerequisites: DNS / Hostnames and IP Reservations
You need either a LAN DNS server that all nodes and clients use, or /etc/hosts entries on all three nodes and all client machines.
Configure:
192.168.0.97 k8s.maksonlee.com
192.168.0.98 app1.maksonlee.com app2.maksonlee.com
192.168.0.99 k8s-1.maksonlee.com k8s-1
192.168.0.100 k8s-2.maksonlee.com k8s-2
192.168.0.101 k8s-3.maksonlee.com k8s-3Also make sure:
192.168.0.97and192.168.0.98are not statically used by any physical host.- They’re excluded from your DHCP range or reserved as static.
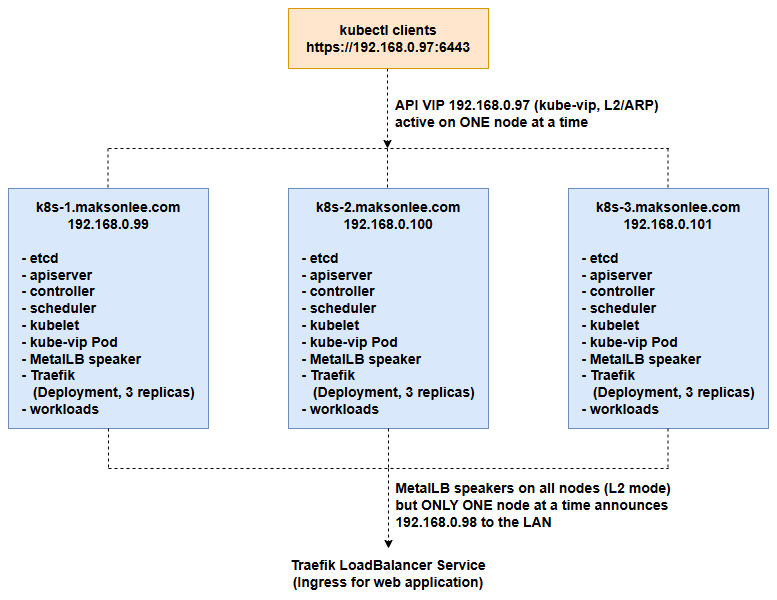
Logical Architecture
At a high level:
- kube-vip runs as a static pod on all three control-plane nodes.
Only one node at a time is leader and announces192.168.0.97(ARP) fork8s.maksonlee.com:6443. - MetalLB speakers run on all nodes in L2 mode; for each LoadBalancer IP (here
192.168.0.98) only one node at a time answers ARP. - Traefik is a
Deploymentwith 3 replicas pluspodAntiAffinityso that, in a 3-node cluster, each node runs exactly one Traefik pod. - Apps are exposed via Ingress on Traefik, and clients reach them with
app1.maksonlee.com/app2.maksonlee.com→192.168.0.98.
- Prepare All Bare-Metal Nodes
Run these steps on k8s-1, k8s-2, and k8s-3.
- Set hostnames
# On k8s-1
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname k8s-1.maksonlee.com
# On k8s-2
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname k8s-2.maksonlee.com
# On k8s-3
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname k8s-3.maksonlee.com- Configure
/etc/hosts
On all nodes:
sudo vi /etc/hostsAdd:
192.168.0.99 k8s-1.maksonlee.com k8s-1
192.168.0.100 k8s-2.maksonlee.com k8s-2
192.168.0.101 k8s-3.maksonlee.com k8s-3- Disable swap
sudo swapoff -a
sudo sed -i '/[[:space:]]swap[[:space:]]/ s/^/#/' /etc/fstab
grep swap /etc/fstab
swapon --show
# optional
sudo rm /swap.img- Kernel modules & sysctl
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/modules-load.d/k8s.conf
overlay
br_netfilter
EOF
sudo modprobe overlay
sudo modprobe br_netfilter
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
EOF
sudo sysctl --system- Install containerd.io (All Nodes)
- Add Docker apt repo & install containerd.io
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc] \
https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(. /etc/os-release && echo "${UBUNTU_CODENAME:-$VERSION_CODENAME}") stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y containerd.io- Configure containerd for SystemdCgroup
sudo mkdir -p /etc/containerd
sudo containerd config default | sudo tee /etc/containerd/config.toml >/dev/nullEdit:
sudo vi /etc/containerd/config.tomlFind:
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc.options]
SystemdCgroup = falseChange to:
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc.options]
SystemdCgroup = trueRestart:
sudo systemctl restart containerd
sudo systemctl enable containerd- Install kubeadm, kubelet, kubectl (All Nodes)
- Add Kubernetes apt repo (v1.34)
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gpg
sudo mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.34/deb/Release.key \
| sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg] https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.34/deb/ /
EOF- Install tools
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl
sudo apt-mark hold kubelet kubeadm kubectl
sudo systemctl enable --now kubelet- Initialize the First Control-Plane (k8s-1)
On k8s-1:
export POD_CIDR=10.244.0.0/16
sudo kubeadm init \
--control-plane-endpoint="192.168.0.99:6443" \
--apiserver-cert-extra-sans="k8s.maksonlee.com,192.168.0.97,192.168.0.99" \
--pod-network-cidr="${POD_CIDR}" \
--upload-certsWhy we DO NOT use k8s.maksonlee.com:6443 here
At this moment kube-vip is not running yet, so the VIP 192.168.0.97 does not exist on the network.
If we initialized the cluster with:
--control-plane-endpoint="k8s.maksonlee.com:6443"then kubeadm would bake that VIP into the cluster configuration, and any new control-plane node trying to join through k8s.maksonlee.com:6443 would talk to an IP that nobody is advertising yet, and the join could fail or hang.
So the bootstrap flow is:
- Init with the real IP of k8s-1 (
192.168.0.99:6443) so the first control-plane comes up cleanly. - Install CNI (Calico) so the node becomes
Ready. - Deploy kube-vip as a static pod so some node starts announcing
192.168.0.97fork8s.maksonlee.com:6443. - Once the VIP is confirmed working, switch the cluster config to use the VIP and then join k8s-2 and k8s-3 via
k8s.maksonlee.com:6443.
Some important details:
k8s.maksonlee.comresolves to192.168.0.97(the VIP).192.168.0.99is the real IP ofk8s-1.maksonlee.com.--apiserver-cert-extra-sans="k8s.maksonlee.com,192.168.0.97,192.168.0.99"ensures the API server certificate is valid for both the real IP and the future VIP/hostname.
From the kubeadm output, save:
- the bootstrap token
- the
discovery-token-ca-cert-hash - the
certificate-key
We’ll use them later to join k8s-2 and k8s-3 as control-plane nodes via the VIP.
- Configure kubectl and Install Calico
- kubectl on k8s-1
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown "$(id -u):$(id -g)" $HOME/.kube/config
kubectl get nodesk8s-1 will show as NotReady until CNI is installed.
- Install Calico v3.31.2
curl -LO https://raw.githubusercontent.com/projectcalico/calico/v3.31.2/manifests/calico.yaml
kubectl apply -f calico.yamlWait:
kubectl get pods -n kube-system
kubectl get nodesk8s-1 should become Ready.
- Deploy kube-vip Static Pod for the API VIP
We use kube-vip to expose a floating API VIP (192.168.0.97) on the bare-metal LAN via k8s.maksonlee.com:6443.
NIC on these nodes is ens32.
- (Optional) pre-pull image (all nodes)
sudo ctr images pull ghcr.io/kube-vip/kube-vip:v1.0.2- Generate manifest on k8s-1
export VIP=192.168.0.97
export INTERFACE=ens32
sudo ctr run --rm --net-host \
ghcr.io/kube-vip/kube-vip:v1.0.2 \
kube-vip /kube-vip manifest pod \
--interface ${INTERFACE} \
--address ${VIP} \
--controlplane \
--arp \
--leaderElection \
| sudo tee /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-vip.yamlCheck:
kubectl get pods -n kube-system -o wide | grep kube-vip- Verify VIP on k8s-1
ip a | grep 192.168.0.97 || echo "VIP not on this node"
kubectl --server=https://192.168.0.97:6443 get nodes- Edit kubeadm-config ConfigMap
kubectl edit cm kubeadm-config -n kube-systemIn the editor, find the ClusterConfiguration section. It should look similar to:
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3
kind: ClusterConfiguration
...
controlPlaneEndpoint: "192.168.0.99:6443"
...Change it to:
controlPlaneEndpoint: "k8s.maksonlee.com:6443"Save and exit.
- Update local kubeconfig to talk to the VIP
kubectl config set-cluster kubernetes --server=https://k8s.maksonlee.com:6443- Copy manifest to k8s-2 and k8s-3
From k8s-1:
scp /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-vip.yaml k8s-2.maksonlee.com:/tmp/
scp /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-vip.yaml k8s-3.maksonlee.com:/tmp/On k8s-2:
sudo mkdir -p /etc/kubernetes/manifests
sudo mv /tmp/kube-vip.yaml /etc/kubernetes/manifests/On k8s-3:
sudo mkdir -p /etc/kubernetes/manifests
sudo mv /tmp/kube-vip.yaml /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-vip pods on k8s-2 / k8s-3 will appear after those nodes join as control-planes.
- Join k8s-2 and k8s-3 as Control-Plane Nodes
On k8s-2:
sudo kubeadm join k8s.maksonlee.com:6443 \
--token <your-token> \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:<your-hash> \
--control-plane \
--certificate-key <your-certificate-key>On k8s-3:
sudo kubeadm join k8s.maksonlee.com:6443 \
--token <your-token> \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:<your-hash> \
--control-plane \
--certificate-key <your-certificate-key>Check from k8s-1:
kubectl get nodes
kubectl get pods -n kube-system -o wide | grep kube-vipYou should see three control-plane nodes and three kube-vip pods.
- Configure kubectl on k8s-2 and k8s-3
On k8s-2:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown "$(id -u):$(id -g)" $HOME/.kube/config
kubectl get nodesOn k8s-3:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown "$(id -u):$(id -g)" $HOME/.kube/config
kubectl get nodes- Allow Workloads on Control-Plane Nodes
Because these bare-metal nodes each serve as both control-plane and worker, remove the default control-plane taint:
kubectl taint nodes --all node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane-Now workloads (including Traefik) can be scheduled on all three nodes.
- Install MetalLB (Layer 2 Mode)
- Deploy MetalLB
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/metallb/metallb/v0.15.2/config/manifests/metallb-native.yaml
kubectl get pods -n metallb-systemYou should see the controller and speaker pods running.
- Configure IPAddressPool & L2Advertisement
Create metallb-l2.yaml:
apiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1
kind: IPAddressPool
metadata:
name: lb-pool
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
addresses:
- 192.168.0.98-192.168.0.98
---
apiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1
kind: L2Advertisement
metadata:
name: lb-l2
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
ipAddressPools:
- lb-poolApply:
kubectl apply -f metallb-l2.yaml
kubectl get ipaddresspools.metallb.io -n metallb-system -o wide- Make Control-Plane Nodes Eligible for MetalLB
kubeadm labels control-plane nodes with:
node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers=MetalLB respects this label and will not announce LoadBalancer IPs from such nodes.
In this bare-metal lab all three nodes should be eligible as LoadBalancer nodes, so remove the label:
kubectl label node k8s-1.maksonlee.com node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers-
kubectl label node k8s-2.maksonlee.com node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers-
kubectl label node k8s-3.maksonlee.com node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers-Check:
kubectl get nodes --show-labels | grep exclude-from-external-load-balancers || echo "no label"- Install Traefik Ingress (3 Replicas, One per Node)
- Install Helm
On your admin node (for example, k8s-1):
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3 | bash
helm repo add traefik https://traefik.github.io/charts
helm repo update
kubectl create namespace traefik- Traefik values: LoadBalancer + 3 replicas + podAntiAffinity
Create traefik-values.yaml:
service:
enabled: true
type: LoadBalancer
spec:
loadBalancerIP: 192.168.0.98
providers:
kubernetesIngress:
enabled: true
ingressClass: traefik
ingressClass:
enabled: true
isDefaultClass: true
deployment:
replicas: 3
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: traefik
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostnameExplanation:
loadBalancerIP: 192.168.0.98pins the Service to the MetalLB pool.replicas: 3matches our 3 bare-metal nodes.requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecutionpodAntiAffinity withtopologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostnameensures that each node can run at most one Traefik pod. With 3 nodes and 3 replicas that means exactly one per node.
(If you prefer to allow multiple Traefik pods on the same node during failures, change this topreferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution.)
- Install or upgrade Traefik
First install:
helm install traefik traefik/traefik \
--namespace traefik \
--create-namespace \
-f traefik-values.yamlLater, if you change the values file:
helm upgrade traefik traefik/traefik \
-n traefik \
-f traefik-values.yamlCheck:
kubectl get deploy traefik -n traefik
kubectl get pods -n traefik -o wide
kubectl get svc traefik -n traefikYou should see:
- Deployment
traefikwith 3/3 replicas available. - Three Traefik pods, each on a different node.
- Service:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
traefik LoadBalancer 10.111.x.x 192.168.0.98 80:3xxxx/TCP,443:3yyyy/TCP ...From a LAN client (for example 192.168.0.67):
curl -v http://192.168.0.98
# Typically: "404 page not found" (Traefik default)If this works, MetalLB and Traefik are reachable from outside the cluster on your bare-metal LAN.
- Deploy Test Web Apps + Ingress
- Namespace
kubectl create namespace apps- Deploy two nginx apps
kubectl create deployment app1 --image=nginx -n apps
kubectl create deployment app2 --image=nginx -n apps
kubectl scale deployment app1 -n apps --replicas=3
kubectl scale deployment app2 -n apps --replicas=3Optional resource limits:
kubectl set resources deployment app1 -n apps \
--requests=cpu=100m,memory=128Mi \
--limits=cpu=500m,memory=512Mi
kubectl set resources deployment app2 -n apps \
--requests=cpu=100m,memory=128Mi \
--limits=cpu=500m,memory=512MiExpose as ClusterIP Services:
kubectl expose deployment app1 -n apps \
--port=80 --target-port=80 --name=app1-svc
kubectl expose deployment app2 -n apps \
--port=80 --target-port=80 --name=app2-svc- Ingress using Traefik
Create apps-ingress.yaml:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: apps-ingress
namespace: apps
spec:
ingressClassName: traefik
rules:
- host: app1.maksonlee.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: app1-svc
port:
number: 80
- host: app2.maksonlee.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: app2-svc
port:
number: 80Apply:
kubectl apply -f apps-ingress.yaml
kubectl get ingress -A
kubectl describe ingress apps-ingress -n appsYou should see the Ingress using traefik as its class and 192.168.0.98 as the address.
- Test from a LAN client
curl -v http://app1.maksonlee.com
curl -v http://app2.maksonlee.comYou should see nginx welcome pages served through Traefik and MetalLB from your bare-metal cluster.
Did this guide save you time?
Support this site